What Mechanism Powers The Rising Phase Of An Action Potential?
Phases Of An Action Potential – Resting Potential, Threshold, Rising, Falling, \U0026 Recovery Phases
Keywords searched by users: What mechanism underlies the rising phase of an action potential Action potential, Resting membrane potential, Neuron action potential, why does regeneration of the action potential occur in one direction, rather than in two directions?, Action potential là gì, Hyperpolarization, Resting potential action potential, Depolarization
What Causes The Rising Phase Of The Action Potential?
The rising phase of the action potential is initiated by a critical voltage change in the axonal membrane known as the threshold. When this threshold is reached, it triggers the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels. These channels allow an influx of sodium ions into the axon, leading to the rapid increase in voltage and the upward trajectory of the action potential. It’s important to note that this influx of sodium ions not only contributes to the rising phase of the action potential but also has the additional effect of depolarizing adjacent regions of the axon. This coordinated sequence of events is fundamental to understanding the underlying mechanisms of action potentials in neurons.
What Is The Rising Action Of The Action Potential?
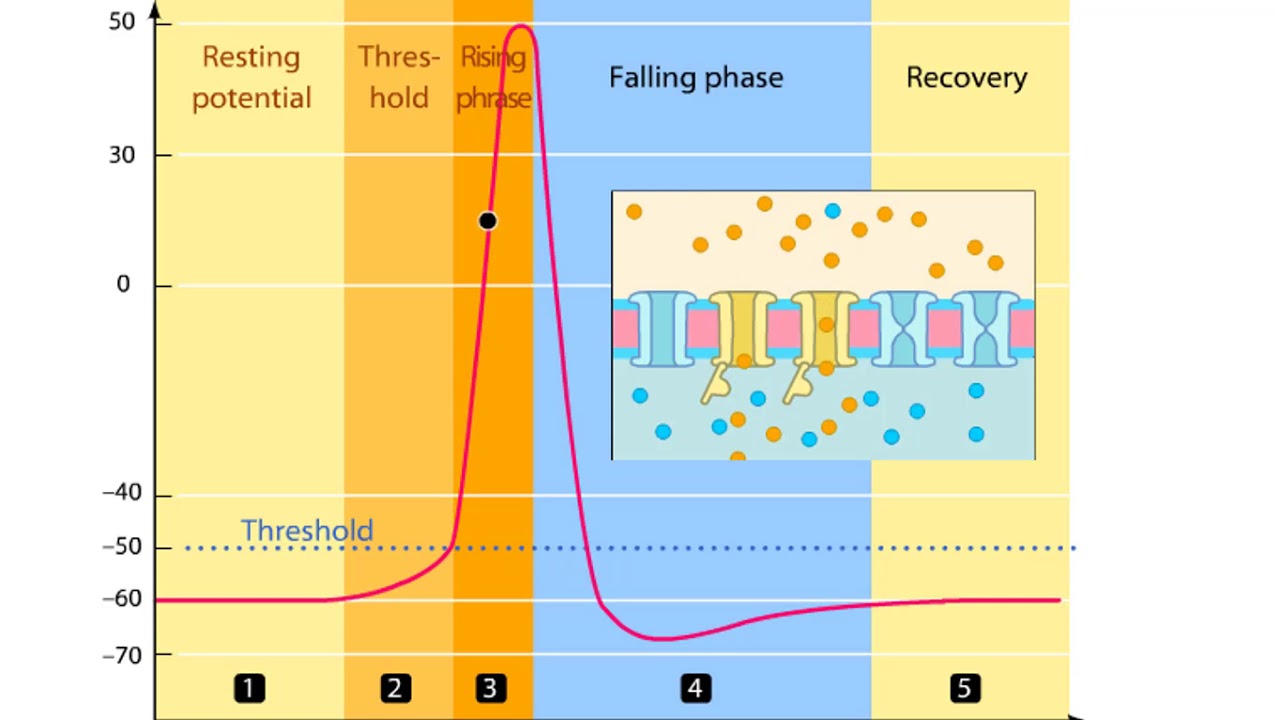
The action potential is a complex electrical event in nerve cells and muscle fibers. Its rising action, also known as the depolarizing phase or upstroke, is the initial stage characterized by a rapid increase in membrane potential. During this phase, the membrane potential moves from its resting state to a peak amplitude. This peak, occurring around 0 mV, marks the overshoot phase, where the membrane potential briefly surpasses its normal voltage.
Subsequently, the repolarization phase commences, where the membrane potential gradually returns to its resting potential. This repolarization is essential for the neuron or muscle fiber to be ready for another potential action. Understanding the dynamics of these phases is crucial for grasping the intricacies of action potentials and their role in transmitting signals within the nervous system and muscle contraction.
What Is The Rising Phase Of An Action Potential Mediated Mainly By?
Nerve Conduction and the Rising Phase of Action Potentials
In the context of nerve conduction, it is crucial to understand the mechanisms behind the rising phase of an action potential. This phase primarily relies on the activity of sodium ions (Na+), specifically Na+ currents. These sodium ions play a pivotal role in the depolarization of the neuronal membrane, a fundamental process in the transmission of electrical signals along axons. During the rising phase, the influx of sodium ions causes a rapid change in the membrane potential, leading to the initiation and propagation of the action potential. This phenomenon is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system and underlies various physiological processes and sensory perceptions. By comprehending the involvement of sodium ions in the rising phase of action potentials, we gain a deeper insight into the intricate workings of neural communication.
Share 43 What mechanism underlies the rising phase of an action potential




Categories: Summary 17 What Mechanism Underlies The Rising Phase Of An Action Potential
See more here: xetaycon.net
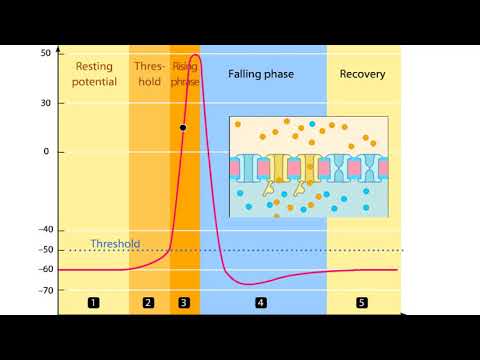
The depolarization, also called the rising phase, is caused when positively charged sodium ions (Na+) suddenly rush through open voltage-gated sodium channels into a neuron. As additional sodium rushes in, the membrane potential actually reverses its polarity.A voltage change that reaches threshold will cause voltage-gated sodium channels to open in the axonal membrane. The influx of sodium causes the rising phase of the action potential, but the ion flow also depolarizes nearby axon regions.The initial or rising phase of the action potential is called the depolarizing phase or the upstroke. The region of the action potential between the 0 mV level and the peak amplitude is the overshoot. The return of the membrane potential to the resting potential is called the repolarization phase.
Learn more about the topic What mechanism underlies the rising phase of an action potential.
- 10.5E: The Action Potential and Propagation
- Action Potentials – Foundations of Neuroscience
- Chapter 1: Resting Potentials & Action Potentials
- Action Potential – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
- Action Potential Flashcards | Quizlet
- Action potential – Wikipedia
See more: https://xetaycon.net/category/climate/